Monday, October 31, 2011
Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis (EV)
Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis is a rare autosomal recessive inherited skin disorder that is characterized by eruptions of wart-like lesions that may occur anywhere on the body. A common name usually heard with this disease is tree man disorder because the symptoms on the body appear as bark-like lesions. The lesions are caused by an infection with the human papillomavirus. There are over 70 different types of HPV that are responsible for causing a wide range of viral warts. It has been found that patients with EV have an abnormal or impaired immune response to HPV or wart viruses. A major concern for patients with EV is that the wart-like lesions may transform into skin cancers.
EV is an autosomal recessive inherited disorder, which means that 2 abnormal EV genes (one from each parent) are needed to have this disease. Ten percent of the EV cases comes from marriages between blood relatives (the patents share a common ancestor). In few cases, sex-linked and autosomal dominant inheritance patterns have also been found.
The warts usually start to develop sometime during childhood. Only 7.5% of cases appear in infancy while 22.5% appear in puberty. The disease affects both males and females and people of all races. The lesions have been described as flat, wart -like lesions that look like plane warts. Flat wart lesions also commonly appear on sun-exposed areas such as the hands, feet, face, and ear lobes. Plaque-like lesions usually appear on the trunk, neck, arms, and legs. The palms, soles, armpits and external fenitals may also be involved. In most cases the warts occur in clusters and can be anything from a few warts to over a hundred.
EV is a lifelong disease, even though the lesions can be treated or removed as they appear, patients will still continue to develop the lesions throughout life. In many cases lesions may develop and remain unchanged for years. There is no current treatment to prevent new EV lesions from occurring. The management of EV involves a combination of medical and surgical treatments alongside patient counseling and education.
Thursday, October 27, 2011
Robinow Syndrome
Robinow Syndrome is another rare disorder that affects the skeletal development and many other parts of the body. It is extremely generic disorder characterized by short-limbed dwarfism, abnormalities in the head, face, and external genitalia. There are two tpes of Robinow syndrome, which are distinguished by the severity of their symptoms and signs and by their patters of inheritance.
The first type is Autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome which is characterized by skeletal abnormalties including the shortening of the long bones in the arms and legs, particularly in the forearms; abnormally short fingers and toes; wedge-shaped spin bones; missing ribs; short stature; and distinctive facial feature. The second type is Autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome which has similar symptoms but tend to be milder than those of the recessive from. Abnormalities of the spine and ribs are rarely seen in the dominany form and this form is less frequent to have.
Medican conditions include frequent ear infections, hearing loss, hypotonia, developmental problems, respiratory problems, eating difficulties, light sensitivity, and esophageal reflux. It has been that both male and female patients have had children with this rare disease. Robinow syndrome is so rare that fewer thatn 200 are affected and reported worldwide.
The first type is Autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome which is characterized by skeletal abnormalties including the shortening of the long bones in the arms and legs, particularly in the forearms; abnormally short fingers and toes; wedge-shaped spin bones; missing ribs; short stature; and distinctive facial feature. The second type is Autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome which has similar symptoms but tend to be milder than those of the recessive from. Abnormalities of the spine and ribs are rarely seen in the dominany form and this form is less frequent to have.
Medican conditions include frequent ear infections, hearing loss, hypotonia, developmental problems, respiratory problems, eating difficulties, light sensitivity, and esophageal reflux. It has been that both male and female patients have had children with this rare disease. Robinow syndrome is so rare that fewer thatn 200 are affected and reported worldwide.
Wednesday, October 19, 2011
Debys-Drash Syndrome
Debys-Drash syndrome (DDS) is a disorder with three main parts: Kidney disease present at birth, Wilms tumor (a kidney cancer), and a malformation of the sexual organs. This syndrome is a genetic disorder that is caused by mutations in the Wilms tumor gene.
Kidney disease: Infants with Denys-Drash syndrome usually are diagnosed with kidney disease between 2 weeks and 18 months of age. These children develop nephrotic syndrome because the kidney tissue becomes hardened and scarred. They may also develop high blood pressure because of this particular disease.
Wilms Tumor: This is a concerous tumor that grows on the kidneys. Almost all of the children with Denys-Drash syndrome develop Wilms tumor on one of both of their kidneys. Usually it is diagnosed at around 2 years of age.
Sexual organ malformation: Both the sexual organs inside the body and those on the outside can be malformed. Boys may have a very tiny penis with undescended malformed testicles, and girls may have enlarged labia and malformed ovaries. Children with this syndrome are at high risk for developing cancer in these malformed tissues.
To be diagnosed with this particular syndrome there are usually symptoms that show:
- Swelling of the parts of the body, especially the abdomen
- Very little urination
- Protein in the urine
- High blood Pressure
- Swollen abdomen and abdominal pain
- Blood in the urine
- A lump or mass in the abdomen
- Abnormal outer genitalia can be seen at birth.
Tuesday, October 11, 2011
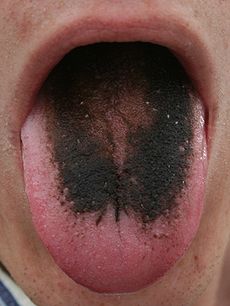
Black Hairy Tongue
Black Hairy Tongue is a disorder that is actually very common and harmless. This disorder is the lengthening of the papilla which is the bumps on the surface of your tongue. Usually the ends of the papilla get rubbed away by food or actually shed off but sometimes they grow much longer than normal, making the tongue look furry. These tiny hair-like projections can grow to 15 times their normal length.
Black hairy tongue is caused by bacteria or fungi in the mouth which makes the tongue appear hairy and black. Normally your papillas are pinkish-white but as they grow, pigments from drinks, food and possibly bacteria get caught in the papilla which dyes the tongue a color. Most often that color is black but it could also be brown, yellow, green or a variety of other colors.
Certain lifestyle habits and conditions can make people more likely to develop black hairy tongue. They include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Drinking a lot of tea or coffee
- Smoking tobacco
- Being dehydrated
- Not producing enough saliva
- Taking medications such as Pepto-Bismol or other chemical bismuth based medications
- Regularly using mouthwash that contains peroxide or menthol
Black hairy tongue is more common in men, people who use intravenous drugs, or those who are HIV-positive. Other than the appearance of the tongue most people do not have any symptoms or feel any discomfort. Some people do complain of a tickling feeling in the back of the roof of their mouth, a metallic taste in their mouth, or even nausea. In more severe cases, the condition may lead to a gagging feeling and food could get caught inside of the long papilla. The best treatment of this condition is to practice good oral hygiene and gently brush your tongue with a soft toothbrush.
Call your doctor or dentist if the problem doesn’t get better on its own because doctors may prescribe antibiotics or antifungal drugs to help get rid of the problem. If the drugs and medication doesn’t improve your tongue, the papilla can be surgically clipped off with a lase or electrosurgery.
Thursday, October 6, 2011
Twin-toTwin Transfusion Syndrome
Twin-to-Twin Transfusion syndrome occurs specifically in identical twins that share the same placenta. The twins share not only the same placenta but some of the same circulation which allows the transfusion of blood from one twin to the other. The donor twin becomes small and anemic, and the other twin becomes large and overloaded with blood. This is estimated to occur in 5-10% of identical twin pregnancies and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms to the mother may include rapidly, enlarging abdomen over 2-3 weeks, premature labor and premature rupture of membranes. This scary disease may be suspected if a pregnant woman carrying twins finds her abdomen enlarging rapidly or it may also be able to be detected by an ultrasound examination of the uterus. Before birth it is possible to seal off some or all of the blood vessels the twins share using a laser but this requires operating while the fetuses are still in the womb which could be very dangerous to the life of the two twins and mother. Treatment after birth may be critical because newborns with twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome may be seriously ill at birth and require treatment in a intensive care unit.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)